Electric Force and Coulomb’s Law
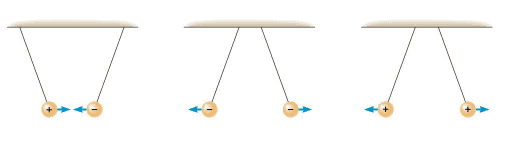
Like charges repel and unlike charges attract each other.
Like other forces that we have encountered, the electric force (also sometimes called the electrostatic force) can alter the motion of an object. It can do so by contributing to the net external force $\sum \vec{F}$ that acts on the object. Newton's second law, $\sum \vec{F} = m \vec{a}$ , specifies the acceleration $\vec{a}$ that arises because of the net external force. Any external electric force that acts on an object must be included when determining the net external force to be used in the second law.
Digital lab: How Do Electric Charges Interact?
|
Digital lab: How Can Static Electric Charges Affect Each Other?
|
|---|---|
Digital figure: Two charges
|
Coulomb's Law
The Force That Point Charges Exert on Each Other
The electrostatic force that stationary charged objects exert on each other depends on the amount of charge on the objects and the distance between them. Experiments reveal that the greater the charge and the closer together they are, the greater is the force.
The French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb (1736-1806) carried out a number of experiments to determine how the electric force that one point charge applies to another depends on the amount of each charge and the separation between them. His result, now known as Coulomb's law.
Adding Electric Forces; Principle of Superposition
Up to now, we have been discussing the electrostatic force on a point charge $\left | q_1 \right |$ due to another point charge $\left | q_2 \right |$. Suppose that a third point charge $\left | q_3 \right |$ is also present. What would be the net force on $q_1$ due to both $q_2$ and $q_3$? It is convenient to deal with such a problem in parts. First, find the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on $q_1$ by $q_2$ (ignoring $q_3$). Then, determine the force exerted on $q_1$, by $q_3$ (ignoring $q_2$). The net force on $q_1$, is the vector sum of these forces.
Animated Physics: Coulomb's Law
|
Concept Map: Electric Force
|
Solution Tutor: Coulomb's Law
|
|---|---|---|
Interactive Demonstration: The Superposition Principle
|
Interactive Demonstration: Coulomb's Law
|
Interactive Demonstration: Electrostatic Equilibrium
|
Digital simulation: Three Charhe's in a Plan
|
You don`t have permission to comment here!
Report